پرونده:DNA Repair.jpg

اندازهٔ این پیشنمایش: ۴۶۷ × ۶۰۰ پیکسل. کیفیتهای دیگر: ۱۸۷ × ۲۴۰ پیکسل | ۵۰۰ × ۶۴۲ پیکسل.
پروندهٔ اصلی (۵۰۰ × ۶۴۲ پیکسل، اندازهٔ پرونده: ۱۰۹ کیلوبایت، نوع MIME پرونده: image/jpeg)
تاریخچهٔ پرونده
روی تاریخ/زمانها کلیک کنید تا نسخهٔ مربوط به آن هنگام را ببینید.
| تاریخ/زمان | بندانگشتی | ابعاد | کاربر | توضیح | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| کنونی | ۲۷ ژانویهٔ ۲۰۰۷، ساعت ۰۱:۱۱ | 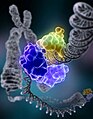 | ۵۰۰ در ۶۴۲ (۱۰۹ کیلوبایت) | DO11.10 | {{Information |Description= DNA damage, due to environmental factors and normal metabolic processes inside the cell, occurs at a rate of 1,000 to 1,000,000 molecular lesions per cell per day. A special enzyme, DNA ligase, encircles the |
کاربرد پرونده
صفحههای زیر از این تصویر استفاده میکنند:
کاربرد سراسری پرونده
ویکیهای دیگر زیر از این پرونده استفاده میکنند:
- کاربرد در ar.wiki.x.io
- کاربرد در ast.wiki.x.io
- کاربرد در ba.wiki.x.io
- کاربرد در be.wiki.x.io
- کاربرد در bg.wiki.x.io
- کاربرد در bs.wiki.x.io
- کاربرد در ca.wiki.x.io
- کاربرد در cs.wiki.x.io
- کاربرد در cy.wiki.x.io
- کاربرد در da.wiki.x.io
- کاربرد در de.wiki.x.io
- کاربرد در el.wiki.x.io
- کاربرد در en.wiki.x.io
- DNA ligase
- DNA repair
- User:Liveste
- User:Bci2
- Molecular models of DNA
- User:Bci2/Books/Wk2Book
- User:Bci2/Books/Wk3vol1
- User:Bci2/Books/Wk4
- User:Bci2/Books/Biophysical Chemistry and Theoretical Biophysics Vol1
- User:Bci2/Books/Biophysical Chemistry and Theoretical Biophysics Volume 1
- User:Bci2/Books/Biophysical Chemistry , Nuclear Medicine and Theoretical Biophysics Vol 1
- User:Bci2/Books/Biophysical Chemistry and Theoretical Biophysics Vol 1
- User:Bci2/Books/Biophysical Chemistry, Nuclear Medicine and Theoretical Biophysics Vol 1 pp318
- User:Bci2/Books/Biophysical Chemistry, Nuclear Medicine and Theoretical Biophysics Vol 1 v3
- Talk:Molecular models of DNA/Galleries
- User:Bci2/Books/StructuralTechniques
- Simon Boulton
- 2021 in science
- April–June 2021 in science
- کاربرد در en.wikibooks.org
- کاربرد در en.wikinews.org
- کاربرد در en.wikiquote.org
نمایش استفادههای سراسری از این پرونده.
